26 Jan 2025: Added health check to the reverse proxy.
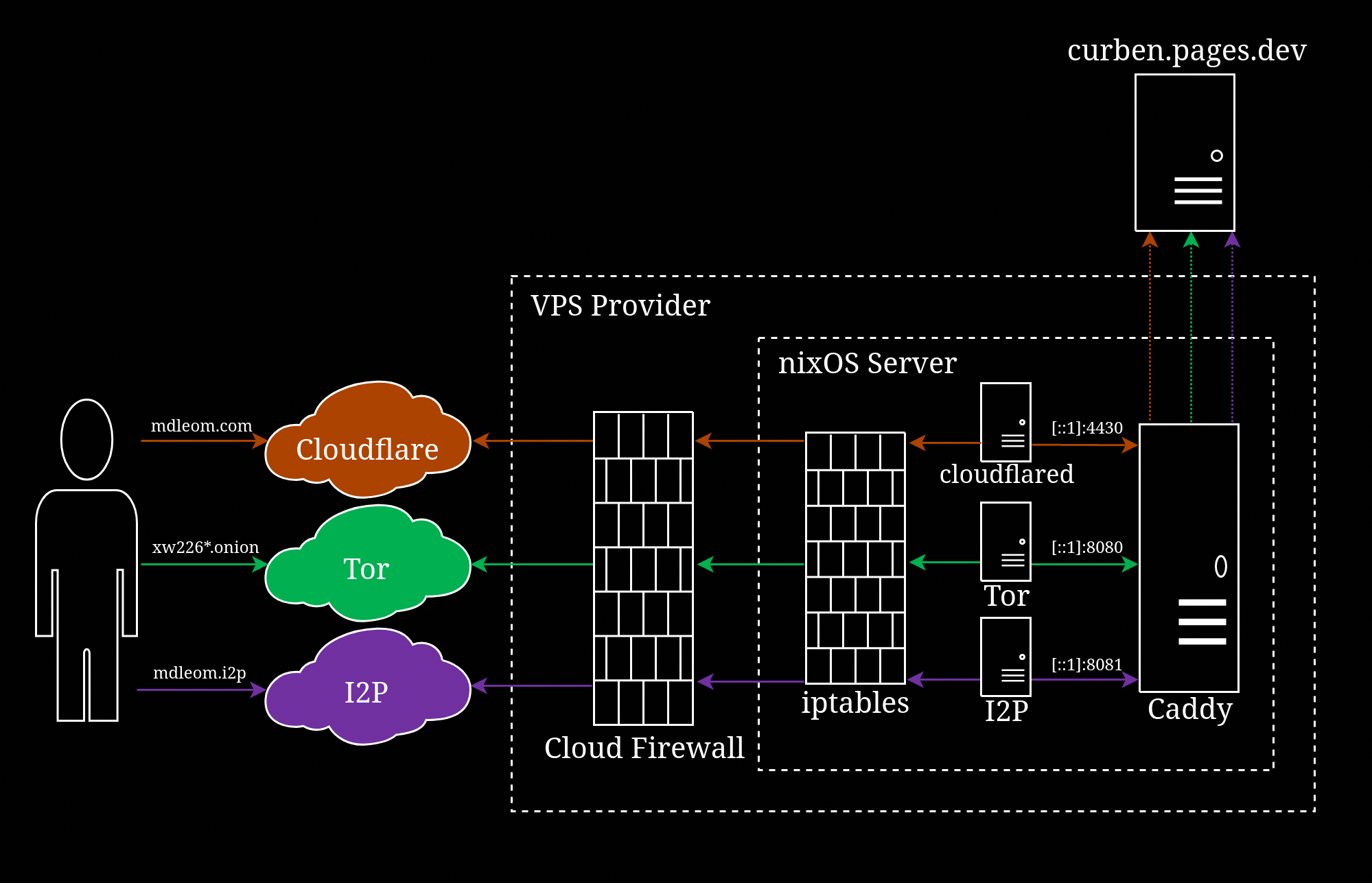
In this segment, I show you how I set up this website (mdleom.com) to reverse proxy to curben.netlify.app using Caddy on NixOS (see above diagram). If you’re not using NixOS, simply skip to the Caddyfile section.
This post is Part 2 of a series of articles that show you how I set up Caddy and Tor hidden service on NixOS:
- Part 1: Install NixOS
- Part 2: Configure NixOS
- Part 3: Configure Caddy
- Part 4: Configure Tor
- Part 5: Configure I2P
Background §
In NixOS, Caddy can be easily configured through “configuration.nix”, without even touching a Caddyfile, if you have a rather simple setup. For example, to serve static files from “/var/www/“ folder,
configuration.nixservices.caddy = {
enable = true;
email = [email protected];
config =
''
example.com {
root /var/www/
}
'';
}Once rebuild, caddy will run as a systemd service. This config also automatically enable HTTPS on example.com using Let’s Encrypt cert which will be stored in “/var/lib/caddy/“ folder by default.
The magic behind the option is “caddy.nix“ which exposes the services.caddy option. It also take care of creating a systemd unit file and installation the caddy package, so you don’t need to install it beforehand. caddy.nix is bundled with NixOS so you can use services.caddy straightaway.
This shows the declarative property of NixOS. Nix, the package manager behind NixOS, also enables the system to be atomic. Imagine putting the whole system binaries under Git or file system snapshot. If you botch the system upgrade, you can easily rollback to previous state (usually via Grub menu).
A package is installed in /nix/store/<hash>/ folder and that hash is what makes Nix atomic. I mention this atomic thing because a package’s binary is only symlink to $PATH (“/usr/bin”) when installed using environment.systemPackages option or nix-env. In this case, “caddy.nix” simply specify the required binary “pkgs.caddy/bin/caddy” and NixOS will automatically install the required package. Since the caddy binary is not available under $PATH, running $ caddy command will return “command not found” error. If you need to use the caddy binary, you have three options:
- Locate the binary in “/nix/store” by checking
$ systemctl status caddy. This is only available when caddy service is enabled in “configuration.nix”. Disabling the service will remove the package. - Install it as a system package using
environment.systemPackages. - Install it as a user package using Home Manager (recommended), ad-hoc shell or
$ nix-env -iA nixpkgs.caddy(discouraged).
caddy.nix grants CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE capability which is not needed in my use case because I’m not binding caddy to port < 1024.
caddyProxy.nix §
I created another nix file which is similar to “caddy.nix”, but without CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE capability. I also removed Let’s Encrypt-related options since I’m using Cloudflare origin certificate. I renamed the options.services.caddy to options.services.caddyProxy to avoid clash with “caddy.nix”. Save the file to “/etc/caddy/caddyProxy.nix” with root as owner. We’ll revisit this file in “configuration.nix“ section later in this guide.
/etc/caddy/caddyProxy.nix{ config, lib, pkgs, ... }:
with lib;
let
cfg = config.services.caddyProxy;
in {
options.services.caddyProxy = {
enable = mkEnableOption "Caddy web server";
config = mkOption {
default = "/etc/caddy/caddyProxy.conf";
type = types.str;
description = "Path to Caddyfile";
};
adapter = mkOption {
default = "caddyfile";
example = "nginx";
type = types.str;
description = ''
Name of the config adapter to use.
See https://caddyserver.com/docs/config-adapters for the full list.
'';
};
dataDir = mkOption {
default = "/var/lib/caddyProxy";
type = types.path;
description = ''
The data directory, for storing certificates. Before 17.09, this
would create a .caddy directory. With 17.09 the contents of the
.caddy directory are in the specified data directory instead.
'';
};
package = mkOption {
default = pkgs.caddy;
defaultText = "pkgs.caddy";
type = types.package;
description = "Caddy package to use.";
};
};
config = mkIf cfg.enable {
systemd.services.caddyProxy = {
description = "Caddy web server";
after = [ "network-online.target" ];
wants = [ "network-online.target" ]; # systemd-networkd-wait-online.service
wantedBy = [ "multi-user.target" ];
startLimitIntervalSec = 14400;
startLimitBurst = 10;
serviceConfig = {
ExecStart = "${cfg.package}/bin/caddy run --config ${cfg.config} --adapter ${cfg.adapter}";
ExecReload = "${cfg.package}/bin/caddy reload --config ${cfg.config} --adapter ${cfg.adapter}";
Type = "simple";
User = "caddyProxy";
Group = "caddyProxy";
Restart = "on-abnormal";
# < 20.09
# https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/pull/97512
# StartLimitIntervalSec = 14400;
# StartLimitBurst = 10;
NoNewPrivileges = true;
LimitNPROC = 512;
LimitNOFILE = 1048576;
PrivateTmp = true;
PrivateDevices = true;
ProtectHome = true;
ProtectSystem = "full";
ReadWriteDirectories = cfg.dataDir;
KillMode = "mixed";
KillSignal = "SIGQUIT";
TimeoutStopSec = "5s";
};
};
users.users.caddyProxy = {
home = cfg.dataDir;
createHome = true;
};
users.groups.caddyProxy = {
members = [ "caddyProxy" ];
};
};
}Caddyfile §
Caddy web server is configured using a Caddyfile. The Caddyfile format I’m using is only compatible with Caddy v1. I will update to v2 once the stable version is released on NixOS. Note that v1 and v2 are incompatible with each other.
Cloudflare origin cert §
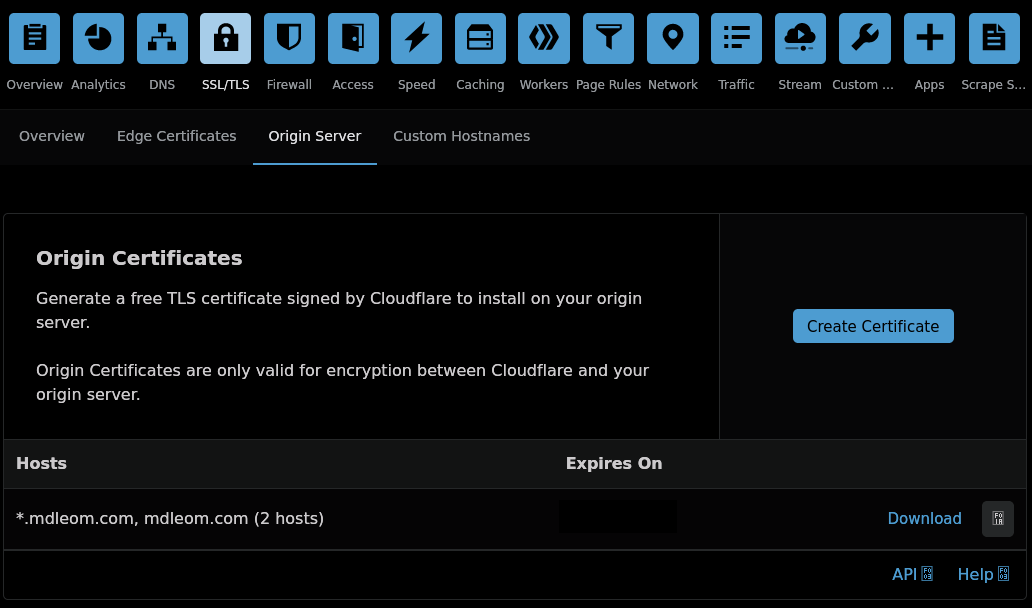
For TLS setup, I’m using Cloudflare Origin Certificate. This cert is only valid for connection between Cloudflare and the origin server (i.e. my web server) because it’s not signed by a CA. The cert is only signed by Cloudflare and does not have a valid chain of trust. TLS connection between a visitor and Cloudflare is enabled by Cloudflare Universal SSL which has a valid cert.
I’m using “Full (strict)” mode which requires either origin cert or a valid cert signed by a trusted CA. This mode forbids self-signed cert unlike “Full” mode. Let’s Encrypt cert is compatible with “Full (strict)”. However, putting a web server behind a CDN means that Caddy could only obtain a Let’s Encrypt using DNS challenge not the default HTTP challenge. Setting up the DNS challenge requires installing tls.dns.cloudflare Caddy plugin which is not included in the NixOS package. The plugin also requires access to my Cloudflare’s API key which I’m not really comfortable with. Hence, the use of Origin Certificate.
Download certs §
Generate and download the cert from Cloudflare Dash → SSL/TLS → Origin Server → Create Certificate. You can choose the validity from 1 week to 15 years. I choose 1 year so I need to repeat this process every year. Make sure you have both certificate (.pem) and private key (.key).
I also use Authenticated Origin Pull which utilize TLS client authentication. A client must present a client certificate that is signed by a private key; in this case, it is signed by Cloudflare itself. The client certificate can be verified using Cloudflare’s public key available here.
By now, you should have three files:
<domain>.pem<domain>.keyorigin-pull-ca.pem
Move the files to home folder of “caddyProxy” user, which is “/var/lib/caddyProxy” in this case. Set the files’ owner and group to caddyProxy and permission to 600.
# chown caddyProxy:caddyProxy /var/lib/caddyProxy/*
# chmod 600 /var/lib/caddyProxy/*If you followed my Part 2 guide, you should have caddyProxy user and group before executing chown and chmod. If you haven’t, check out this section of Part 2.
Initial setup §
Set up Caddy to listen on apex domain and www.* on port 4430
Caddyfilemdleom.com:4430 www.mdleom.com:4430 { }
Enable HTTPS §
Subsequent configurations (directives) shall be inside the curly braces. Let’s start with tls directive.
mdleom.com:4430 www.mdleom.com:4430 {
tls /var/lib/caddyProxy/mdleom.com.pem /var/lib/caddyProxy/mdleom.com.key {
protocols tls1.3
client_auth {
mode require_and_verify
trusted_ca_cert_file /var/lib/caddyProxy/origin-pull-ca.pem
}
}
}Redirect www to apex §
Connection to www.mdleom.com is redirected to mdleom.com with HTTP 301 status.
@www host www.mdleom.com
redir @www https://mdleom.com{uri} permanent{label1} placeholder refers to the first part of the request hostname, e.g. if hostname is foo.bar.com, {label1} is foo, {label2} is bar and so on.
{uri} is used to retain the path when redirecting. www.mdleom.com/foo/bar is redirected to mdleom.com/foo/bar.
If you prefer to redirect apex to www,
@www host mdleom.com
redir @www https://www.mdleom.com{uri} permanentReverse proxy §
Aside from reverse proxy to random mirrors, I utilise Cloudflare Images (hosted at mdleom.com/images/*) for on-the-fly image processing. However, this service is not available on my website in the dark web since the traffic is not proxied through Cloudflare.
As a workaround, I configured Caddy to route /images/* to curben.pages.dev (which will then route to mdleom.com/images/*). I could route directly to mdleom.com/images/*, but that could cause request loops.
handle /images/* {
import reverseProxy curben.pages.dev
}
handle_path /screenshot/* {
# "curben.netlify.app" is updated to "mdleom.com"
rewrite * /screenshot/mdleom.com{path}
reverse_proxy https://cdn.statically.io
}
handle_path /files/* {
rewrite * /curben/blog/-/raw/site{path}
reverse_proxy https://gitlab.com
}
reverse_proxy https://curben.pages.dev https://curben.netlify.app {
(see the last section for load-balancing)
}rewrite directive is necessary to remove screenshot/* and files/* from the path, so that “mdleom.com/files/foo.pdf” is linked to “https://cdn.statically.io/files/foo.pdf“, not “https://cdn.statically.io/files/files/foo.pdf“.
Another issue is navigating to a mirror that does not route through Cloudflare (Images) nor Caddy, so image resizing does not work, e.g. https://curben.netlify.app/images/foo.jpg will return 404. My workaround is to route /images/* to the root path which is where the original images are hosted.
source/_redirects_redirects/images/* /:splat 200 /screenshot/* https://cdn.statically.io/screenshot/curben.netlify.app/:splat 200 /files/* /:splat 200
Host header §
To make sure Caddy sends the correct Host: header to the upstream/backend locations, I use header_up option,
reverse_proxy https://curben.pages.dev https://curben.netlify.app {
header_up Host {http.reverse_proxy.upstream.host}
}Add or remove headers §
To prevent any unnecessary request headers from being sent to the upstreams, I use header_up. I use it to remove cookie, referer and other headers added by Cloudflare. Since there are many headers to remove, I group them as a global variable. I apply it to all reverse_proxy directives.
(removeHeaders) {
header_up -cookie
header_up -referer
(see the last section for complete headers)
}
mdleom.com {
reverse_proxy https://curben.pages.dev https://curben.netlify.app {
import removeHeaders
}
}The upstream locations insert some information into the response headers that are irrelevant to the site visitors. I use header directive to filter them out. It also applies to all reverse_proxy directives.
header {
-cf-cache-status
-cf-ray
(see the last section for complete headers)
defer
}I also add the Cache-Control and Referrer-Policy to the response header. Use minus (-) sign before each option to remove particular header. Without minus sign, the specified header is either added or replacing an existing one.
Cache-Control §
/libs folder contains third-party libraries. Since the library is usually requested by a specific version, we can safely assume that the response would remain the same. This means I can set long expiration and immutable on the response. immutable is to tell the browser that revalidation is not needed.
header {
Cache-Control "max-age=86400, public"
}
header /libs/* {
Cache-Control "public, max-age=31536000, immutable"
}Intercept HTTP 302 redirect §
GitLab Pages returns HTTP 302 to redirect to https://projects.gitlab.io/auth?domain=https://<username>.gitlab.io&state=<random-base64> when navigating to an invalid path (e.g. https://curben.gitlab.io/blog/invalid-path). To prevent the redirect, I configured Caddy to intercept any HTTP 300-399 and return HTTP 404 instead.
reverse_proxy https://curben.pages.dev https://curben.netlify.app {
@error3xx status 3xx
handle_response @error3xx {
respond "" {rp.status_code}
}
}Complete Caddyfile §
Since I also set up reverse proxy for Tor Onion and I2P Eepsite, I refactor most of the configuration into “common.conf” and import it into “caddyProxy.conf”.
common.conf{ ## disable admin endpoint # admin off ## http->https redirect # auto_https disable_redirects ## Remove PII from error log log { level ERROR format filter { wrap json { time_format rfc3339 } fields { request>remote_ip delete request>remote_port delete request>headers>CDN-Loop delete request>headers>CF-Cache-Status delete request>headers>CF-Connecting-IP delete request>headers>CF-IPCountry delete request>headers>CF-RAY delete request>headers>CF-Request-ID delete request>headers>CF-Visitor delete request>headers>CF-Worker delete request>headers>Client-IP delete request>headers>Cookie delete request>headers>Forwarded delete request>headers>Referer delete request>headers>Sec-CH-UA-Arch delete request>headers>Sec-CH-UA-Bitness delete request>headers>Sec-CH-UA-Full-Version delete request>headers>Sec-CH-UA-UA delete request>headers>Sec-CH-UA-UA-Mobile delete request>headers>Sec-CH-UA-UA-Model delete request>headers>Sec-CH-UA-UA-Platform delete request>headers>Sec-CH-UA-UA-Platform-Version delete request>headers>True-Client-IP delete request>headers>User-Agent delete request>headers>Via delete request>headers>X-Forwarded-For delete request>headers>X-Forwarded-Host delete request>headers>X-Forwarded-Proto delete request>headers>X-ProxyUser-Ip delete } } } } (setHeaders) { -accept-ch -access-control-allow-origin -access-control-expose-headers -alt-svc -cdn-cache -cdn-cachedat -cdn-edgestorageid -cdn-pullzone -cdn-requestcountrycode -cdn-requestid -cdn-requestpullcode -cdn-requestpullsuccess -cdn-uid -cf-bgj -cf-cache-status -cf-chl-out -cf-mitigated -cf-polished -cf-ray -cf-request-id -content-disposition -critical-ch -etag -expect-ct -fly-request-id -gitlab-lb -gitlab-sv -nel -origin-agent-cluster -report-to -server -server-timing -set-cookie -st-cache -st-id -strict_sni -strict_sni_header -timing-allow-origin -via -x-amz-server-side-encryption -x-bytes-saved -x-cache -x-cache-hits -x-download-options -x-gitlab-feature-category -x-nextjs-cache -x-nf-request-id -x-permitted-cross-domain-policies -x-powered-by -x-request-id -x-robots-tag -x-runtime -x-served-by -x-server -x-timer -x-ua-compatible Cache-Control "max-age=86400, public" Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; child-src 'none'; connect-src 'none'; font-src 'none'; frame-src 'none'; img-src 'self'; manifest-src 'self'; media-src 'none'; object-src 'none'; prefetch-src 'none'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; worker-src 'none'; base-uri 'none'; form-action https://duckduckgo.com https://duckduckgogg42xjoc72x3sjasowoarfbgcmvfimaftt6twagswzczad.onion; frame-ancestors 'none'; block-all-mixed-content" Expires "0" Permissions-Policy "accelerometer=(), ambient-light-sensor=(), attribution-reporting=(), autoplay=(), bluetooth=(), browsing-topics=(), camera=(), compute-pressure=(), cross-origin-isolated=(), display-capture=(), document-domain=(), encrypted-media=(), fullscreen=(), gamepad=(), geolocation=(), gyroscope=(), hid=(), identity-credentials-get=(), idle-detection=(), local-fonts=(), magnetometer=(), microphone=(), midi=(), otp-credentials=(), payment=(), picture-in-picture=(), publickey-credentials-create=(), publickey-credentials-get=(), screen-wake-lock=(), serial=(), speaker-selection=(), storage-access=(), usb=(), web-share=(self), window-management=(), xr-spatial-tracking=(), interest-cohort=()" Referrer-Policy "no-referrer" X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" X-Frame-Options "DENY" X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" } (removeHeaders) { header_up -cdn-loop header_up -cf-cache-status header_up -cf-connecting-ip header_up -cf-ipcountry header_up -cf-ray header_up -cf-request-id header_up -cf-visitor header_up -cf-worker header_up -client-ip header_up -cookie header_up -forwarded header_up -referer # https://user-agent-client-hints.glitch.me/ header_up -sec-ch-ua-arch header_up -sec-ch-ua-bitness header_up -sec-ch-ua-full-version header_up -sec-ch-ua-ua header_up -sec-ch-ua-ua-mobile header_up -sec-ch-ua-ua-model header_up -sec-ch-ua-ua-platform header_up -sec-ch-ua-ua-platform-version header_up -sec-gpc header_up -true-client-ip header_up -via header_up -x-forwarded-for header_up -x-forwarded-host header_up -x-forwarded-proto header_up -x-proxyuser-ip header_up Host {http.reverse_proxy.upstream.host} header_up User-Agent "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)" } (reverseProxy) { reverse_proxy https://{args.0} { import removeHeaders header_up Host {http.reverse_proxy.upstream.host} } } (pathProxy) { @staticFiles { path *.css *.gif *.ico *.jpg *.js *.pdf *.png *.svg *.webp } header @staticFiles { Cache-Control "max-age=604800, public" defer } header /libs/* { Cache-Control "max-age=31536000, public, immutable" defer } # resize image on darkweb handle /images/* { import reverseProxy curben.pages.dev } handle_path /screenshot/* { rewrite * /screenshot/mdleom.com{path} import reverseProxy cdn.statically.io } handle_path /files/* { rewrite * /curben/blog/-/raw/site{path} import reverseProxy gitlab.com } # Multiple mirrors reverse_proxy https://curben.pages.dev https://curben.netlify.app https://curben.gitlab.io https://curbengh.github.io { import removeHeaders lb_policy random lb_retries 2 health_uri / health_interval 30s health_status 2xx } }
caddyProxy.confimport common.conf ## mdleom.com mdleom.com:4430 www.mdleom.com:4430 { tls /var/lib/caddyProxy/mdleom.com.pem /var/lib/caddyProxy/mdleom.com.key { protocols tls1.3 client_auth { mode require_and_verify trusted_ca_cert_file /var/lib/caddyProxy/origin-pull-ca.pem } } # www -> apex @www host www.mdleom.com redir @www https://mdleom.com{uri} permanent header { import setHeaders Onion-Location "http://xw226dvxac7jzcpsf4xb64r4epr6o5hgn46dxlqk7gnjptakik6xnzqd.onion" Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" defer } import pathProxy }
configuration.nix §
One last thing to do is to import “caddyProxy.nix“ and enable services.caddyProxy.
/etc/nixos/configuration.nixrequire = [ /etc/caddy/caddyProxy.nix ];
services.caddyProxy = {
enable = true;
config = "/etc/caddy/caddyProxy.conf";
};